这个小节的目标是添加光线相光内容,根据光线打在屏幕上不同的位置,生成一张蓝白渐变图。

我们可以将光线理解为一条射线,从某个点作为起点,向某个方向发射。例如,从三维世界 (0,0,0)点起始,向(-1,1,2)的方向发射。
博客中的一张图是这样的
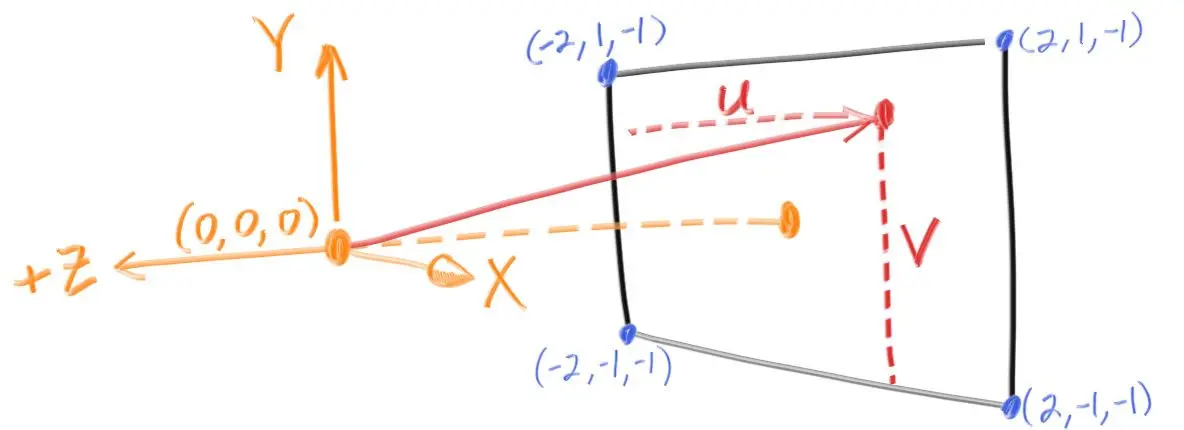
摄像机在(0,0,0)点,坐标正 Y 向上,正 X 向右,正 Z 向屏幕外。从摄像机的位置,向摄像机视口,坐标(U,V)的点,发射一条射线,然后就是计算UV这个点的像素颜色。
vec3.rs 的代码做了微小的改动,重载了对于f64类型计算的操作符,然后给Vec3这个结构体起了一个别名 Color,用来描述 RGB 颜色。
// /src/vec3.rs
use std::ops::{Add, AddAssign, Div, DivAssign, Mul, MulAssign, Neg, Sub, SubAssign};
#[derive(Debug, Copy, Clone)]
pub struct Vec3 {
pub x: f64,
pub y: f64,
pub z: f64,
}
impl Vec3 {
pub fn zero() -> Self {
Self {
x: 0.0,
y: 0.0,
z: 0.0,
}
}
pub fn one() -> Self {
Self {
x: 1.0,
y: 1.0,
z: 1.0,
}
}
pub fn new(x: f64, y: f64, z: f64) -> Self {
Self { x, y, z }
}
pub fn length_squared(&self) -> f64 {
self.x * self.x + self.y * self.y + self.z * self.z
}
pub fn length(&self) -> f64 {
self.length_squared().sqrt()
}
fn to_u64(&self) -> (u64, u64, u64) {
let x = (self.x * 255.999) as u64;
let y = (self.y * 255.999) as u64;
let z = (self.z * 255.999) as u64;
(x, y, z)
}
pub fn get_color_string(&self) -> String {
let xyz = self.to_u64();
format!("{} {} {}\n", xyz.0, xyz.1, xyz.2)
}
pub fn dot(u: Vec3, v: Vec3) -> f64 {
u.x * v.x + u.y * v.y + u.z * v.z
}
pub fn cross(u: Vec3, v: Vec3) -> Self {
Self {
x: u.y * v.z - u.z * v.y,
y: u.z * v.x - u.x * v.z,
z: u.x * v.y - u.y * v.x,
}
}
pub fn unit_vector(v: Self) -> Self {
v / v.length()
}
}
impl Neg for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {
Self {
x: -self.x,
y: -self.y,
z: -self.z,
}
}
}
impl Add for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn add(self, other: Self) -> Self {
Self {
x: self.x + other.x,
y: self.y + other.y,
z: self.z + other.z,
}
}
}
impl AddAssign for Vec3 {
fn add_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {
*self = Self {
x: self.x + other.x,
y: self.y + other.y,
z: self.z + other.z,
}
}
}
impl Sub for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn sub(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {
Self {
x: self.x - other.x,
y: self.y - other.y,
z: self.z - other.z,
}
}
}
impl SubAssign for Vec3 {
fn sub_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {
*self = Self {
x: self.x - other.x,
y: self.y - other.y,
z: self.z - other.z,
}
}
}
impl Mul<Vec3> for f64 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn mul(self, rhs: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 {
x: rhs.x * self,
y: rhs.y * self,
z: rhs.z * self,
}
}
}
impl Mul<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn mul(self, rhs: f64) -> Self {
Self {
x: self.x * rhs,
y: self.y * rhs,
z: self.z * rhs,
}
}
}
impl Mul for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn mul(self, rhs: Self) -> Self {
Self {
x: self.x * rhs.x,
y: self.y * rhs.y,
z: self.z * rhs.z,
}
}
}
impl MulAssign<f64> for Vec3 {
fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: f64) {
*self = Self {
x: self.x * rhs,
y: self.y * rhs,
z: self.z * rhs,
};
}
}
impl DivAssign<f64> for Vec3 {
fn div_assign(&mut self, rhs: f64) {
*self = Self {
x: self.x / rhs,
y: self.y / rhs,
z: self.z / rhs,
};
}
}
impl Div<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn div(self, rhs: f64) -> Self {
Self {
x: self.x / rhs,
y: self.y / rhs,
z: self.z / rhs,
}
}
}
pub type Color = Vec3;
然后添加描述光线的类,新建 ray.rs 文件,在里面添加下面的代码。一条光线,有一个起点 origin,和一个方向 direction。
// src/ray.rs
use crate::vec3::Vec3;
#[derive(Debug, Copy, Clone)]
pub struct Ray {
pub origin: Vec3,
pub direction: Vec3,
}
impl Ray {
pub fn new(origin: Vec3, direction: Vec3) -> Self {
Self { origin, direction }
}
// at 函数相当于将光线进行缩放
pub fn at(&self, t: f64) -> Vec3 {
self.origin + self.direction * t
}
}
然后是 main.rs 做了改动,添加了一个 ray_color 函数,这个函数接受一个光线做为参数,然后计算这条光线所产生的颜色。在这里,我们通过使用光线的方向,计算其所在屏幕的UV坐标,然后使用 Blend 公式,来计算这个UV坐标,应该是什么颜色。
Blend 公式是通用的 blendedValue = (1 - t) * startValue + t * endValue
#![allow(dead_code)]
mod ray;
mod vec3;
use ray::Ray;
use vec3::{Color, Vec3};
// ray_color 函数接受一条光线,计算这条光线打在视口
fn ray_color(r: Ray) -> Color {
// 将光线的方向标准化,保证其值在 -1 到 1 之间
let unit_direction = Vec3::unit_vector(r.direction);
// 为了计算方便,我们将方向的 y 值,从 [-1,1] 映射到 [0, 1]
let t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y + 1.0);
// 做一个蓝白渐变,当 t 为 0 时,就是白色,将 t 为 1 时,就是蓝色
return (1.0 - t) * Color::one() + t * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0);
}
fn main() {
// Image config
const ASPECT_RATIO: f64 = 16.0 / 9.0;
const IMAGE_WIDTH: u64 = 400;
const IMAGE_HEIGHT: u64 = ((IMAGE_WIDTH as f64) / ASPECT_RATIO) as u64;
// Camera config
let viewport_height = 2.0;
let viewport_width = ASPECT_RATIO * viewport_height;
let focal_length = 10.0;
let origin = Vec3::zero();
let horizontal = Vec3::new(viewport_width, 0.0, 0.0);
let vertical = Vec3::new(0.0, viewport_height, 0.0);
let lower_left_corner =
origin - horizontal / 2.0 - vertical / 2.0 - Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, focal_length);
// Render
println!("{}", format!("P3\n{} {}\n255\n", IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT));
for j in (0..=IMAGE_HEIGHT - 1).rev() {
for i in 0..IMAGE_WIDTH {
let u = i as f64 / (IMAGE_WIDTH - 1) as f64;
let v = j as f64 / (IMAGE_HEIGHT - 1) as f64;
let direction = lower_left_corner + u * horizontal + v * vertical - origin;
let r = Ray::new(origin, direction);
let pixel_color = ray_color(r);
println!("{}", pixel_color.get_color_string());
}
}
}
最后,使用 cargo run > image2.ppm 就可以生成蓝白渐变图。